-

Regulations
Sequence of Documents
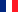
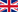
To certify a receiver for a given application requires a series of documents




Glossary
ARAIM: Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring
ARINC: Aeronautical Radio Incorporated (provides aeronautical standard)
CONOPS: A CONcept of OPerationS is a document describing the operational use of a proposed system
DFMC: Dual Frequency Multi Constellation
EASA: European Aviation Safety Agency
EDG²E: Equipment for Dual Frequency Galileo GPS and EGNOS
EGNOS: European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service
ERTMS: European Rail Traffic Management System
ETSO: European Technical Standard Order. Defined by EASA, it gives the requirements that an airborne equipment must meet.
EUROCAE: EURopean Organization for Civil Aviation Equipment
FAA: Federal Aviation Administration (US)
FDE: Fault Detection and Exclusion (detects the presence of a failing satellite and removes it from the positoning)
GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite System
GPS: Global Positioning System
EUSPA: European Union Agency for the Space Programme
ICAO: International Civil Aviation Organization
MOPS: Minimum Operation Performance Standards
PBN: Performance-Based Navigation
PVT: Position, Velocity and Time estimation
RAIM: Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring
RF FRONT END: Radio Frequency frond end
RTCA: Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics
SARPS: Standards and Recommended Practices
SBAS: Space Based Augmentation System
TSO: Technical Standards Orders